High-strength structural bolts are threaded fasteners that are widely used for steel-to-steel component connections in structures such as bridges, construction machinery, and wind turbines.
These applications require fasteners capable of withstanding high loads and tensile stress. Safety inspections of structures and equipment with bolted joints can be a time-consuming, labor-intensive process due to the sheer number of bolts that need to be examined.

The Nuts and Bolts of High-Strength Fasteners
Take the wind power industry, for example. For conventional wind turbine equipment, each rotor blade must be firmly joined to the hub, and up to 160 sets of high-strength bolts are required to connect the three blades. The wind tower is usually composed of three or four sections, which require as many as 400 to 500 sets of high-strength bolts to connect them together and to anchor the base to the grounding platform. Overall, around 600 sets of high-strength bolts are required for the wind turbine’s construction.
Ensuring the Quality and Safety of Structures through Bolt Testing
With such a large number of bolts used in a wind turbine, their quality could directly affect the wind turbine’s quality and safety. The harsh environment in which wind turbines operate exerts various kinds of stresses on the bolts. As the bolts age and wear, their connections tend to loosen and they can develop cracks. When they become severe enough, these defects pose serious risks to the wind turbine’s safe operation. Regular maintenance inspection including fatigue assessment of bolts is necessary to detect cracks at an early stage, so faulty bolts are repaired and replaced before they cause critical damage.

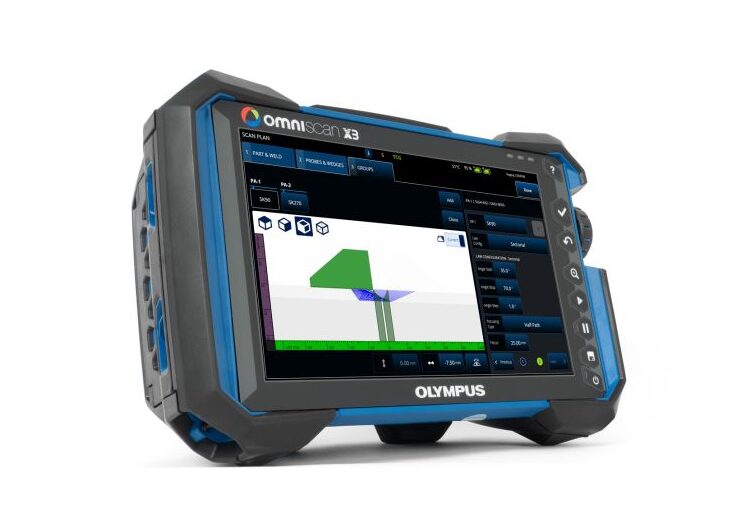
High-Efficiency Bolt Inspection Using the OmniScan™ X3 Flaw Detector
Using the advanced phased array (PA) and total focusing method (TFM) capabilities of the OmniScan X3 phased array detector, inspectors can perform efficient and thorough assessments to validate the integrity of structural bolts. These advanced ultrasonic techniques provide fast, reliable, and repeatable results, helping to reduce the time required to inspect numerous bolts in a structure.
Detecting Cracks and Volumetric Flaws in Bolts Using Phased Array Ultrasound
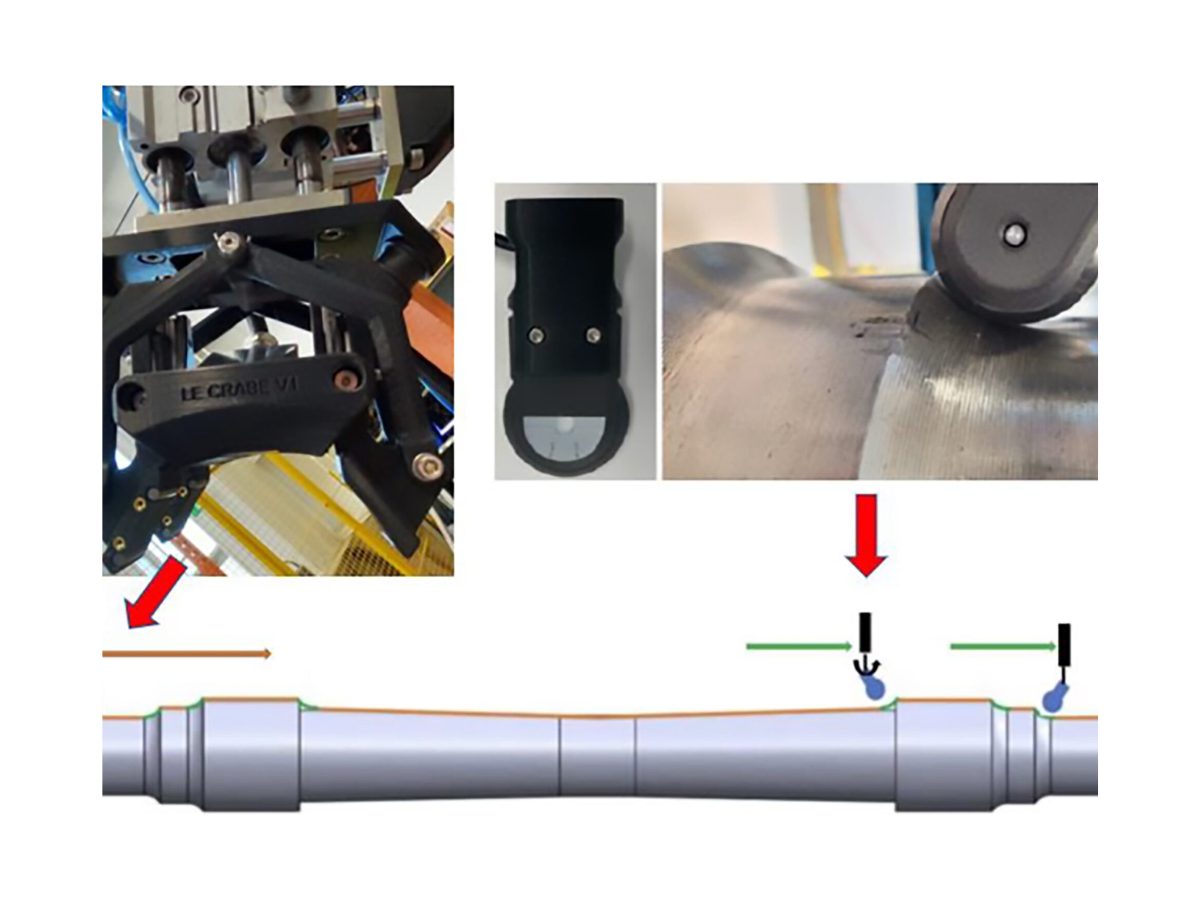
Detecting cracks and other critical defects in the volume of bolts is accomplished using an Olympus phased array probe and the OmniScan X3 flaw detector. Though this example uses a reference tested in our labs, the OmniScan X3 unit is highly portable, so it can easily be carried on site to perform in-service maintenance inspections.
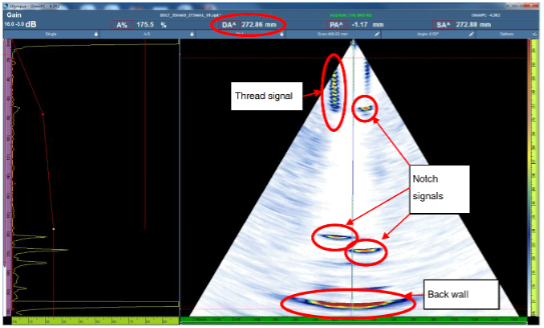
We recently tested a custom phased array ring probe designed specifically for bolt inspection. Finding the right probe for this application is important to achieving a good probability of detection (POD) and reliable results. Download this handy infographic to help you with your selection.
Monitoring the Severity of Surface Corrosion in Bolts Using TFM
Using the innovative total focusing method (TFM) of the OmniScan X3 flaw detector enables inspectors to easily monitor corrosion on the bolt’s surface. Here you can see one of our probes coupled to the surface of the bolt head and the resulting TFM images on the display.
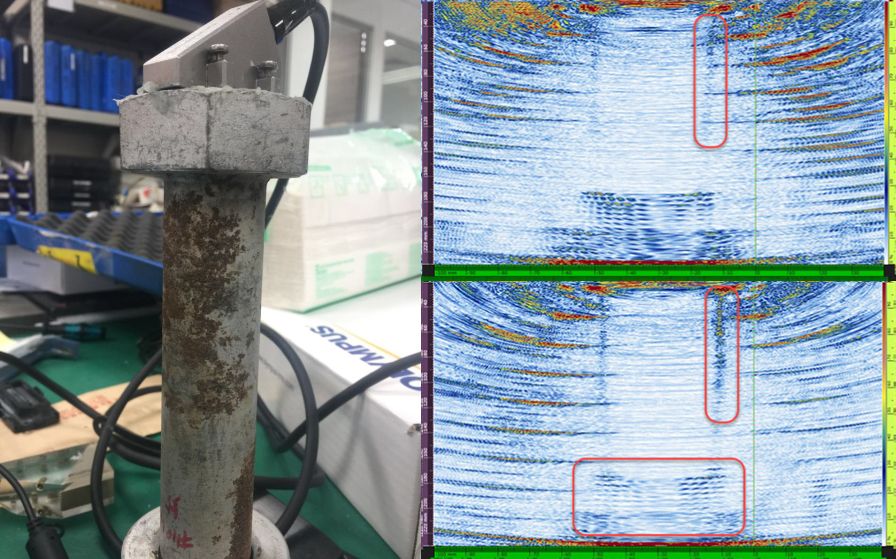
Comparing the top TFM image and the bottom TFM image, we can see clearly see the severity of the corrosion cluster. In the top image, we see the normal surface signal outlined in red. And, and the bottom TFM imaging shows the corrosion (outlined in red near the top) and the thread (outlined in red near the bottom).
Bolt-Testing-Friendly Features of the OmniScan X3 Flaw Detector
Innovative TFM
- Real-time TFM envelope processing improves image clarity
- Up to 1024 × 1024 grid resolution provides images with finer details so flaws in a cluster are more easily distinguishable
- Acoustic Influence Map (AIM) scan plan modelling tool simulates TFM wave set (mode) coverage and reflector sensitivity based on user-specified settings
- Up to 4 TFM mode images are generated using different propagation angles and can be displayed simultaneously, easing flaw sizing and characterisation including depth
Efficiency-Enhancing Phased Array
- 20 kHz maximum pulse repetition frequency enables fast scanning, up to 3x faster than our previous model
- 800% high amplitude range helps reduce the need to rescan
- Compatible with all Olympus’ existing phased array probes and scanners
- On-board support of Dual Linear Array™ (DLA) and Dual Matrix Array™ probes speeds up the setup creation process
Reliable and User-Friendly Operation
- IP65 rated to withstand rain and dust
- Simplified navigation for settings menus and scan plan steps
- 5-hour battery life and hot-swappable batteries
- Wireless network connectivity
For more information and advice about bolt inspection applications and Olympus NDT products, don’t hesitate to contact us to discuss your needs with one of our experts.
This article was originally published by OLYMPUS.