In the world of railway safety, ensuring that tracks and the surrounding environment and structures are in good condition is crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring smooth operations.
To achieve this, various inspection and detection systems are employed to identify potential issues along the railway corridor. However, these systems are always imperfect to some degree and can sometimes produce results that can be confusing. Two important terms for railway inspection techniques and testing that come into play are “true positives” and “false positives.” Let’s break these down in simple terms.
What is a True Positive?
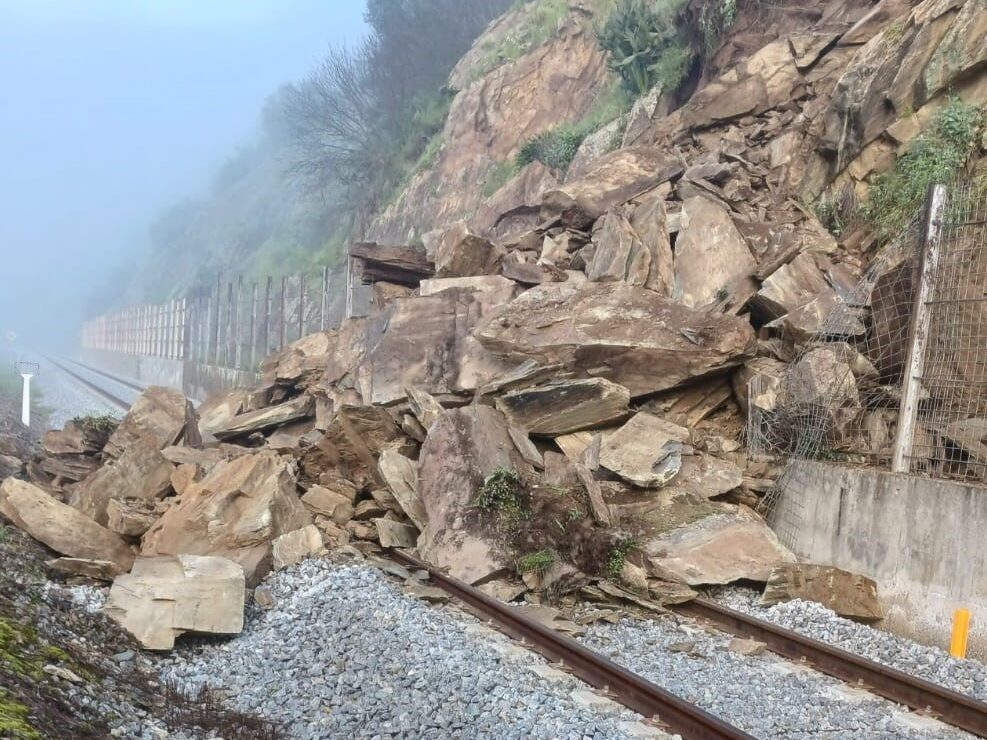
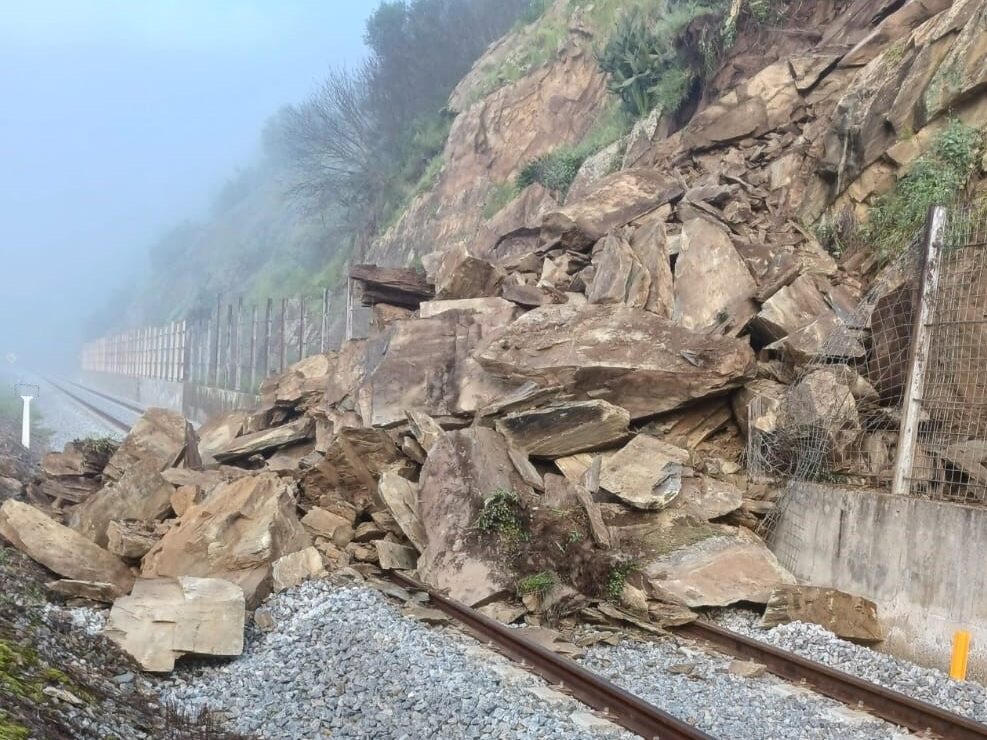
A “true positive” occurs when a detection system correctly identifies a problem that exists on the railway track. For example, imagine a system (such as our DAS system) that detects rockfalls onto the track. If the system alerts the operations or maintenance teams about a rockfall, and upon inspection, they find that there is indeed a rock present on or dangerously near the track, this is a true positive. In this case, the detection system has given a positive indication of a fault/problem that was found by further inspection to be true. True positive indications are what we think of for a fault detection system to allow timely repairs and ensure the safety of trains and passengers.
True positives are essential because they help railway operators maintain the integrity of the tracks and their operations. By accurately identifying real problems, they can act before identified issues lead to accidents or service disruptions.
What is a False Positive?
A “false positive” occurs in a monitoring system when it indicates that there is a problem when, in fact, there isn’t one. Using the same example of the rockfall detection system, if the sensor alerts the maintenance team about a rockfall, but upon inspection, no rock is found endangering the track , this is categorised as a false positive. The system has mistakenly identified a problem which when inspected further, no problem was found.
False positives can be problematic for several reasons. First, they lead to unnecessary inspections, actions (such as speed restrictions for the rockfall example) and sometimes unnecessary repairs , wasting time and resources. Second, if maintenance teams are constantly responding to false alarms, they may become desensitised to alerts, potentially overlooking real issues in the future. This can create a dangerous situation where actual problems go undetected.
The Importance of Balancing True Positives and False Positives
Automated inspection and detection systems generally always have some degree of false positives. In railway systems, like many other industries, the goal is to maximise true positives while minimising false positives. This balance is crucial for effective maintenance and safety. If a system generates too many false positives, it can overwhelm maintenance teams and lead to inefficiencies. Conversely, if a system fails to identify real issues (resulting in false negatives), it can jeopardise safety.
To achieve this balance, we use advanced technologies, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, to improve the accuracy of our detection systems. These technologies can analyse vast amounts of data and learn from past detections, helping to refine the system’s ability to distinguish between real issues and false alarms.
Conclusion
Understanding true positives and false positives when monitoring railway safety. True positives help ensure that real issues are addressed promptly, while false positives can lead to unnecessary work and potential oversight of actual problems. By utilising both advanced detection technologies, machine learning and AI together with extensive railway experience we ensure that railways maintain safe and efficient for everyone. As technology continues to evolve, the hope is that the accuracy of these detection systems will improve, leading to safer journeys for all passengers.
This article was originally published by Sensonic.














