The California High-Speed Rail Authority has presented key developments in its approach to sustainable infrastructure.
The project, which is currently under construction between Merced and Bakersfield, forms part of California’s broader efforts to reduce transport-related emissions and promote economic growth.
Once operational, the high-speed rail system will run on electricity generated entirely from renewable sources and will travel at speeds of up to 220 miles per hour.
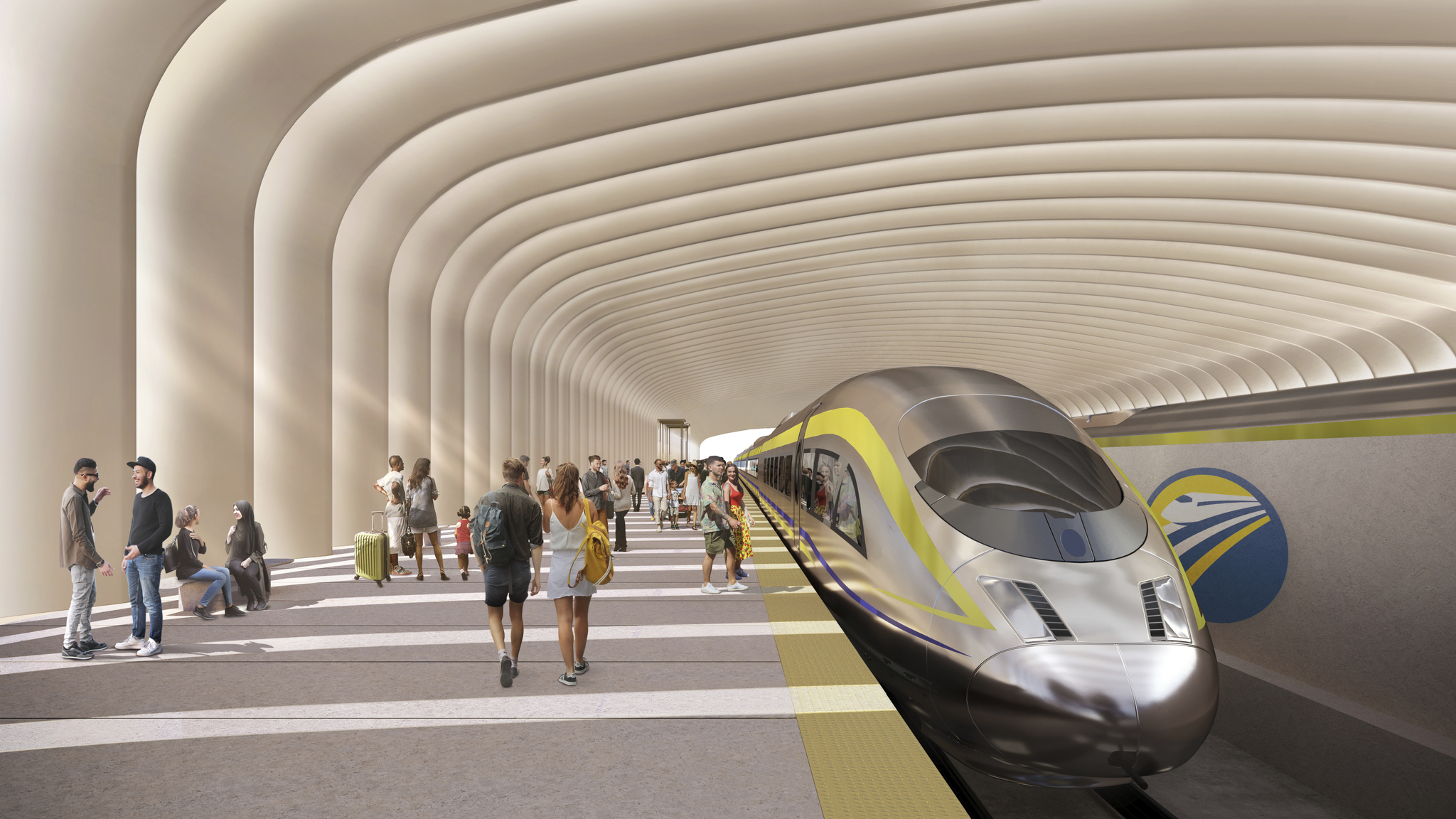

The Authority emphasises that environmental considerations are central not only to its long-term operation but also to its construction methods.
Margaret Cederoth, Director of Planning and Sustainability said:In the spirit of Earth Day, the Authority recognises sustainability as the very core of an electrified, high-speed rail system – an overall critical component of an economically dynamic and carbon-neutral transportation future. Even in construction we’re committed to advancing this program cleanly, with the Authority’s policies and practices leading us to reduce or avoid more equivalent emissions in the Central Valley than have been created so far.
Construction
Efforts to reduce emissions during construction include mandates requiring contractors to use lower-emission equipment, the planting of trees to offset carbon, and the diversion of 95% of non-hazardous construction waste from landfill.
From 2015 to 2023, waste diverted through recycling, reuse, stockpiling and composting totalled more than 300,000 tons, with only 5% sent to landfill.
The Authority is also taking part in California’s Voluntary Emissions Reduction Agreements, which require that any construction-related air pollutants are offset within local air quality districts.
Habitat and Land Protection
To ensure environmental protection, the project’s viaducts and bridges are being built to maintain animal migration routes and waterway access.
Over 4,400 acres of open space have been preserved, including wetlands, and more than 3,000 acres of farmland have been protected through conservation easements.
Energy Resilience
In a recent move, the Authority announced progress on securing a photovoltaic and battery energy storage system for the Central Valley segment. The system is intended to support uninterrupted operations, reduce dependence on the main power grid, and contribute to lower running costs.
Once operational, the rail system is expected to reduce California’s greenhouse gas emissions by up to 3 million metric tons of CO₂ equivalent annually, which is comparable to removing several hundred thousand petrol-powered vehicles from circulation.
Economic and Community Development
The Authority reports that the project has created more than 15,000 jobs so far, with 1,600 workers active on site each day. Around 99% of spending to date has remained in-state, and approximately two-thirds has benefited communities designated as disadvantaged.
The Central Valley Training Center in Selma, set up to provide local workforce training, has seen over 250 graduates. The Authority is also collaborating with cities to shape station area plans that align with local priorities and urban development goals.