As the effects of climate change become more visible, railway systems are increasingly exposed to extreme weather conditions. Events such as heatwaves, floods, snowstorms and sandstorms can impact the reliability and safety of rail operations. Alstom aims to address these risks by developing and adapting solutions across train design, infrastructure, signalling, and maintenance.
Between 2015 and 2022, the number of significant rail incidents in France linked to climate-related hazards reportedly tripled. In light of such trends, efforts to strengthen the resilience of rail networks are gaining attention among operators, manufacturers, and public authorities.
Rolling Stock
Alstom designs its trains to function within a wide range of environmental conditions, following international standards such as EN50125-1 and EN14750. Core rolling stock can operate between -25°C and +45°C, with additional adaptations available for areas experiencing more extreme climates.
For example, metro trains developed for Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, are equipped with cooling systems intended to continue functioning during high ambient temperatures and power interruptions. The design process incorporates materials and systems aimed at maintaining performance and passenger comfort in regions with variable or harsh weather.
Infrastructure
Rail infrastructure is vulnerable to damage from weather-related factors such as water ingress, heat-induced rail stress, or high winds. To address this, Alstom has introduced solutions designed to improve infrastructure durability under such conditions.
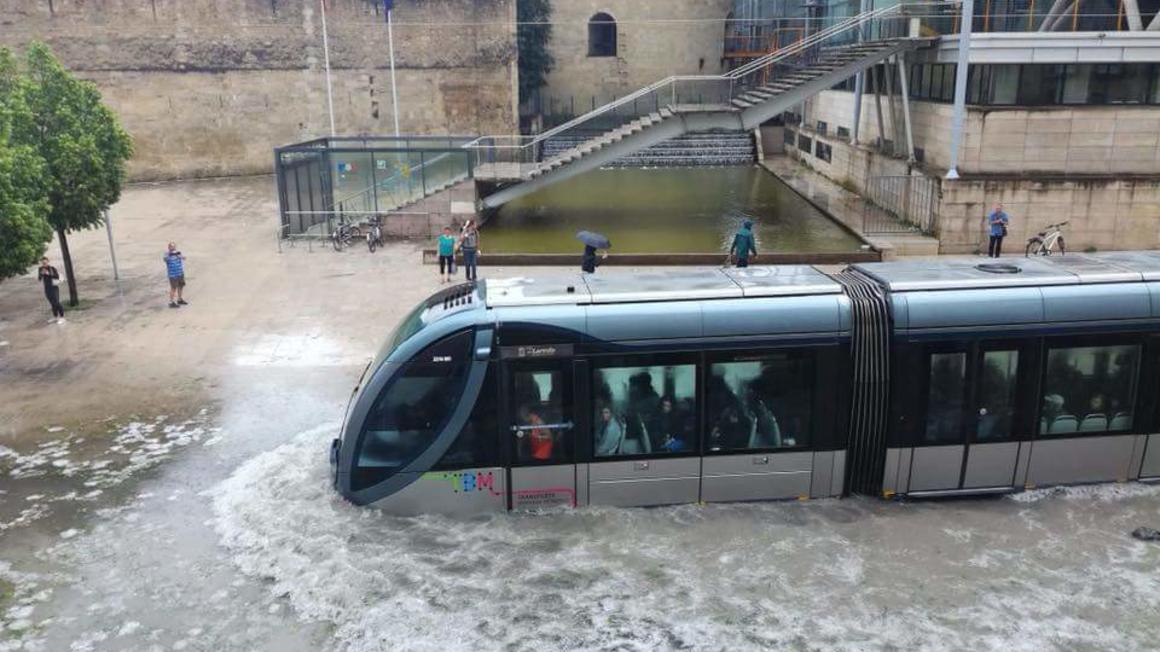
The company’s APS (ground-level power supply) system is one such example. It has been implemented in cities including Dubai, Bordeaux and Istanbul. This system is designed to withstand challenges such as dust accumulation, temporary submersion, and high surface temperatures. In practice, it has supported continued tram operation during events like sandstorms and flooding.

Signalling
To limit exposure of signalling equipment to the elements, Alstom has adopted a train-centric architecture, placing fewer components along the track. This reduces the potential for weather-related failures and supports more consistent service.
In addition, traffic management systems are integrated with local weather data, allowing operators to adjust train speeds and other parameters in response to conditions. To reduce the risk of control centre disruption, Alstom also installs secondary technical rooms in separate locations.
Maintenance Planning
Alstom’s maintenance strategies include predictive and prognostic techniques that make use of real-time and historical data. These methods help identify wear patterns and anticipate component failures.
In Dubai, capacitor replacement schedules have been adjusted from 20 to 10 years to reflect the effect of sustained high temperatures. Other measures include more frequent inspections in cold weather and increased rust protection in high-humidity areas. Trams such as the Flexity range are also tested in environmental chambers in Vienna to assess performance under simulated weather extremes.

Stakeholder Collaboration
Alstom collaborates with operators, regulators, and industry groups to align its efforts with local and international standards. This includes involvement in working groups related to railway applications (EN 50125-5) and air conditioning standards (EN 13129).
Véronique Andries, Vice-President of Sustainability & CSR at Alstom said:Alstom, a global leader in mobility solutions, strongly believes in its role in preventing and mitigating impacts from climate change, which are likely to affect the railway sector: directly, as both transport infrastructure and operations are vulnerable to changes of the current climate conditions and indirectly, as a transition to a low-carbon economy, compatible with the Paris Agreement objectives, may result in strengthened climate regulations for the transport sector.
Preventing these impacts calls for innovative, multi-disciplinary approaches that should assess current vulnerabilities, develop sustainable mitigation techniques and implement adaptative solutions capable of withstanding emerging threats.
Protecting assets and adapting our solutions to specific climate conditions is a critical part of the company’s Sustainability & CSR strategy.
Alstom’s activities reflect a broader focus within the rail industry on planning for long-term climate resilience. By adapting design, infrastructure and maintenance to evolving environmental demands, the company aims to support more reliable and sustainable transport systems in the years ahead.